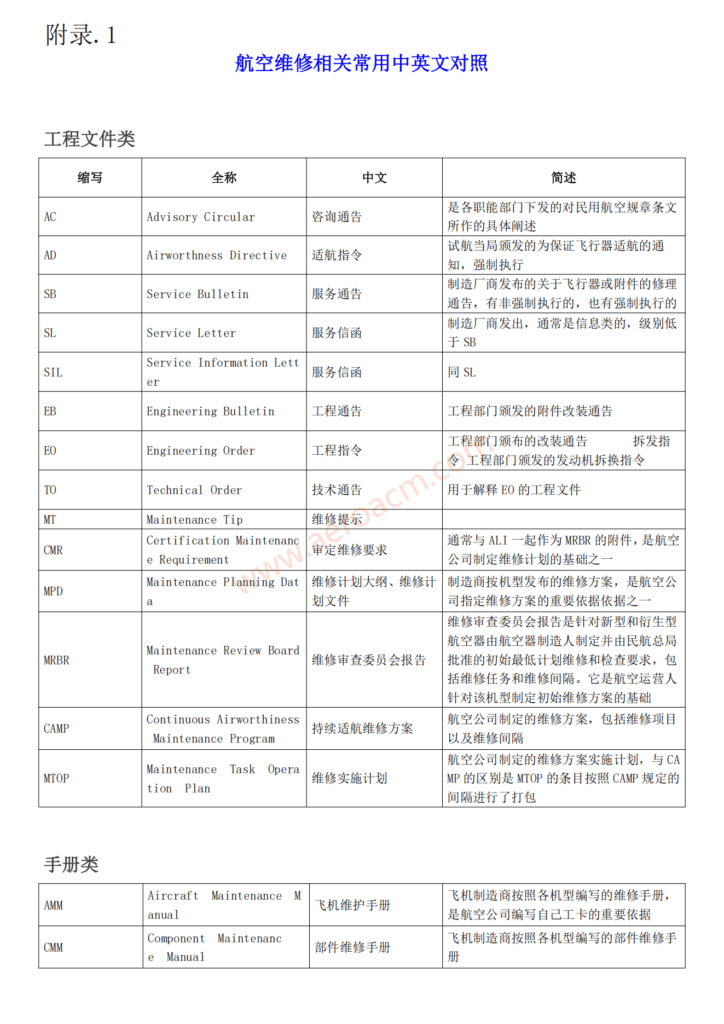
发动机的性能主要表现在推力特性、燃油消耗特性。
The performance of the engine is mainly reflected in thrust characteristics and fuel consumption characteristics.
(1)推力特性
Thrust characteristics
用来表征发动机推力的基本参数有:发动机转速 n 和发动机压力比 EPR。发动机转速增加,推力增大,因此发动机转速大小可以反映发动机的推力大小。高涵道涡轮风扇发动机,由于发动机推力主要由外涵风扇产生,所以常用发动机低压转子速度 N1(即风扇速度)来表征发动机推力大小。发动机压力比用EPR 表示,是指低压涡轮的出口总压与低压压气机进口总压之比,同气流通过发动机的加速成比例。高涵道涡轮风扇发动机,由于发动机推力主要由外涵风扇产生,所以发动机压力比常用外涵风扇出口气体总压与外涵风扇进口气体总压之比。
The basic parameters used to characterize engine thrust are engine speed n and engine pressure ratio EPR. As the engine speed increases, the thrust increases, so the engine speed can reflect the thrust of the engine. For the high bypass turbofan engine, the engine thrust is mainly generated by the external fan, so the low-pressure rotor speed N1 (i.e. fan speed) of the engine is often used to represent the engine thrust. The engine pressure ratio, expressed in EPR, refers to the ratio of the total pressure at the outlet of the low-pressure turbine to the total pressure at the inlet of the low pressure compressor, which is proportional to the acceleration of the air flow through the engine. For the high bypass turbofan engine, the engine thrust is mainly generated by the external fan, so the engine pressure is higher than the ratio of the total gas pressure at the outlet of the common external fan and the total gas pressure at the inlet of the external fan.
(2)燃油消耗特性
Fuel consumption characteristics
涡轮喷气发动机作为热机和推进器的组合体,用总效率来衡量它的燃油经济性。发动机的效率包括发动机热效率、推进效率和总效率。热效率指的是发动机产生的机械功与发动机燃油完全燃烧放出热量之比,表示在热循环中加入的热量有多少转变为机械功,也称内效率。推进效率指的是推进功与可用功之比,也等于推力乘以飞行速度,用来表示发动机产生的可用功有多少变成推进功,这个比值称为推进效率,也称外效率。总效率指的是推进功与燃料完全燃烧放出热量之比,也等于热效率(内效率)与推进效率(外效率)的乘积,用来表示燃油燃烧的热能有多少转化为飞机的动能。
As a combination of heat engine and propeller, the fuel economy of turbojet engine is measured by its total efficiency. Engine efficiency includes engine thermal efficiency, propulsion efficiency and total efficiency. Thermal efficiency refers to the ratio of the mechanical work produced by the engine to the heat released by the complete combustion of the engine fuel, indicating how much heat added in the thermal cycle is converted into mechanical work, also known as internal efficiency. Propulsion efficiency refers to the ratio of propulsion work to available work, which is also equal to thrust times flight speed. It is used to indicate how much of the available work generated by the engine becomes propulsion work. This ratio is called propulsion efficiency, also known as external efficiency. Total efficiency refers to the ratio of propulsion work to the heat released by the complete combustion of fuel, which is also equal to the product of thermal efficiency (internal efficiency) and propulsion efficiency (external efficiency). It is used to indicate how much heat energy from fuel combustion is converted into kinetic energy of aircraft.
考虑发动机的推力特性和燃油经济性,发动机主要用于:
Considering the thrust characteristics and fuel economy of the engine, the engine is mainly used for:
① 涡轴发动机(主要用于直升机)
Turboshaft engine (mainly used for helicopters)
② 涡桨发动机(主要用于支线飞机)
Turboprop engine (mainly used for regional aircraft, military transport aircraft
and unmanned aerial vehicles)
③ 涡扇发动机(主要用于干线飞机和军机)
Turbofan engine (mainly used for trunk aircraft and military aircraft)
④ 涡喷发动机(主要用于军机)
Turbojet engine (mainly used for military aircraft)
![图片[1]-发动机的性能和适用范围 Engine Performance and Scope of Application【转】-航修札记](https://www.aeroacm.cn/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/image-11.png)
![图片[2]-发动机的性能和适用范围 Engine Performance and Scope of Application【转】-航修札记](https://www.aeroacm.cn/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/image-10.png)


暂无评论内容