增压系统——座舱增压控制的原理
Pressurization System-Principle of Cabin Pressurization Control
![图片[1]-座舱增压控制的原理(Principle of Cabin Pressurization Control)【转】-航修札记](https://www.aeroacm.cn/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/image-21-1024x930.png)
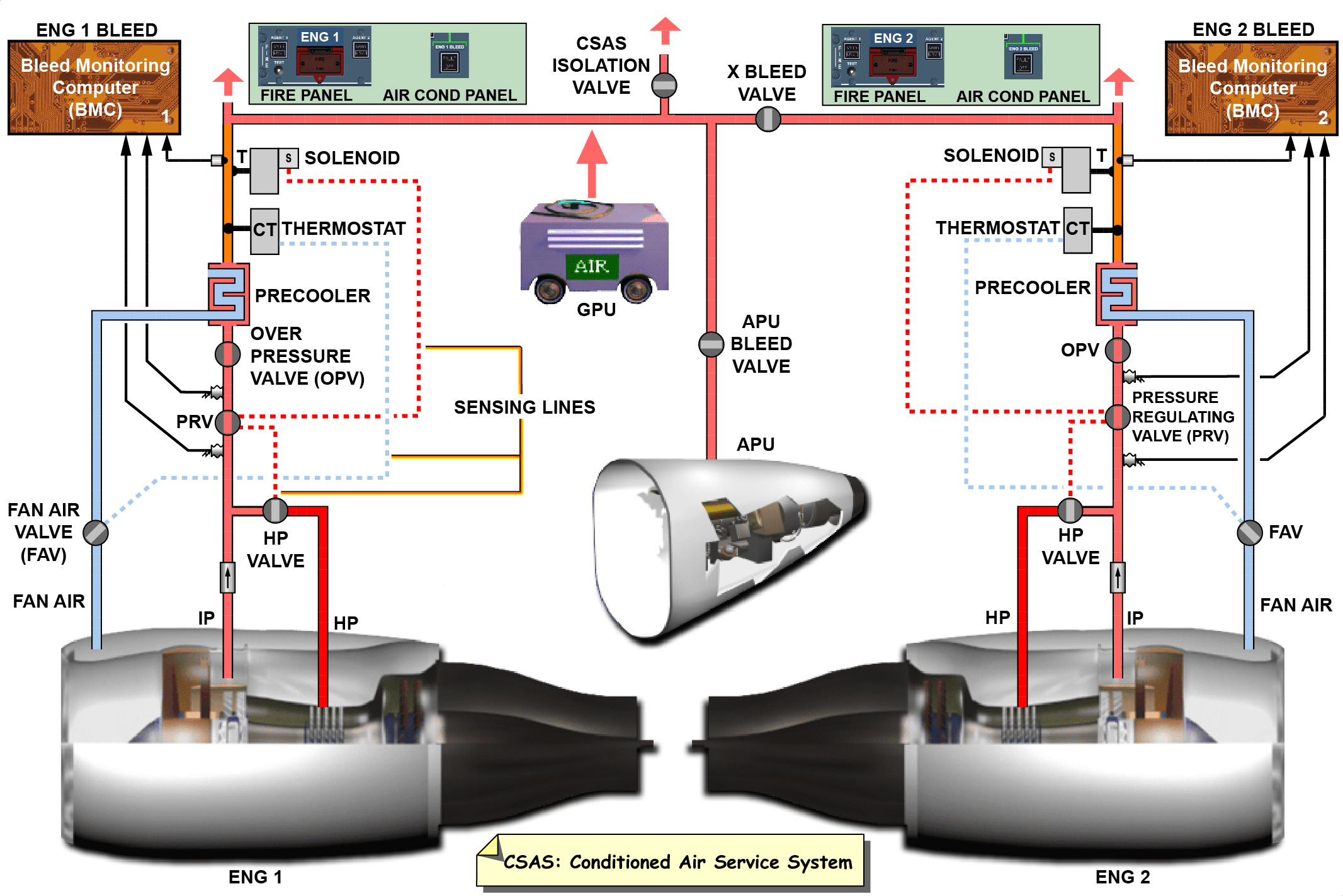
座舱增压系统都由机舱压力控制系统控制。要保持座舱压力不变,必须保持座舱供气量等于排气量与漏气量之和,要使客舱压力增大,就需使座舱供气量大于排气量与漏气量之和,由于漏气量是无法控制的,所以控制座舱压力及其变化速度应通过控制供气量和排气量来实现,除此之外可以通过两个释压活门提供安全释压,限制座舱内外的最大压差。负压释放活门可防止外界大气压力超过机舱内部压力。
The cabin pressurization system is controlled by the cabin pressure control system. To maintain the cabin pressure unchanged, it is necessary to keep the cabin air supply equal to the sum of the air displacement and the air leakage. To increase the cabin pressure, it is necessary to make the cabin air supply greater than the sum of the air displacement and the air leakage. Since the air leakage is uncontrollable, the control of the cabin pressure and its rate of change should be achieved by controlling the air supply and the air displacement. In addition, the safe pressure relief can be provided through two pressure relief valves, Limit the maximum pressure difference inside and outside the cabin. The negative pressure relief valve can prevent the external atmospheric pressure from exceeding the internal pressure of the cabin.
根据适航法规的要求,飞机在最大设计巡航高度上,座舱高度不能大于8000 英尺,而巡航时飞行高度一般在 30000 至 40000 英尺之间,飞机结构承受较大的余压,排气活门同时承受较大的压差。因此,巡航过程中,排气活门开度最小。飞机在地面时,座舱内外压差较小,排气活门开度较大。飞机在爬升或下降过程中,由于其飞行高度的变化,可能导致座舱高度产生突变。在飞机下降过程中,如果座舱高度下降过快,即座舱压力上升率过大,应加快排气活门开启的速率,将座舱内压力降低,抑制压力上升的速率。
According to the requirements of airworthiness regulations, at the maximum design cruise altitude of the aircraft, the cabin altitude cannot be greater than 8000 feet, while the flight altitude during cruise is generally between 30000 and 40000 feet. The aircraft structure bears large residual pressure, and the exhaust valve also bears large differential pressure. Therefore, the exhaust valve opening is the smallest during cruise. When the aircraft is on the ground, the pressure difference inside and outside the cockpit is small, and the opening of the exhaust valve is large. During the climb or descent of the aircraft, the cabin altitude may change suddenly due to the change of its flight altitude. In the process of aircraft descent, if the cabin altitude drops too fast, that is, the cabin pressure rise rate is too high, the opening rate of the exhaust valve should be accelerated to reduce the cabin pressure and inhibit the rate of pressure rise.
![图片[2]-座舱增压控制的原理(Principle of Cabin Pressurization Control)【转】-航修札记](https://www.aeroacm.cn/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/image-22.png)
![图片[3]-座舱增压控制的原理(Principle of Cabin Pressurization Control)【转】-航修札记](https://www.aeroacm.cn/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/image-23-1024x795.png)
座舱压力制度是指飞机座舱内压力(即座舱高度)随飞机飞行高度的变化关系,又称为座舱调压规律。座舱压力制度是座舱压力控制系统处于平衡状态时的静态调节特性。目前民航飞机常用的压力制度有两种:适用于低速飞机的三段式压力制度和现代客机采用的直线式(或近似直线式)压力制度。三段式压力控制制度是指飞行过程中,座舱压力(座舱高度)随飞行高度(或外界大气压力)成三段变化,如图 2 所示。直线式压力制度是当飞机从地面爬升到巡航高度时,座舱压力随飞机飞行高度的增加成直线关系均匀变化,如图 3 所示。飞机在未达到巡航高度前,座舱余压缓慢增加,当飞机进入巡航高度时,座舱余压达到座舱余压限制值。
The cabin pressure system refers to the relationship between the cabin pressure (i.e. the cabin altitude) and the flight altitude of the aircraft, also known as the cabin pressure regulation law. The cabin pressure system is a static regulation characteristic when the cabin pressure control system is in equilibrium. At present, there are two pressure systems commonly used in civil aviation aircraft: the three-stage pressure system applicable to low-speed aircraft and the linear (or nearly linear) pressure system used by modern passenger aircraft. Three-stage pressure control system means that the cabin pressure (cabin altitude) changes in three stages with flight altitude (or external atmospheric pressure) during flight, as shown in Figure 2. The linear pressure system is that when the aircraft climbs from the ground to the cruise altitude, the cabin pressure changes uniformly in a linear relationship with the increase of the aircraft flight altitude, as shown in Figure 3. Before the aircraft reaches the cruise altitude, the cabin residual pressure increases slowly. When the aircraft enters the cruise altitude, the cabin residual pressure reaches the cabin residual pressure limit.


暂无评论内容