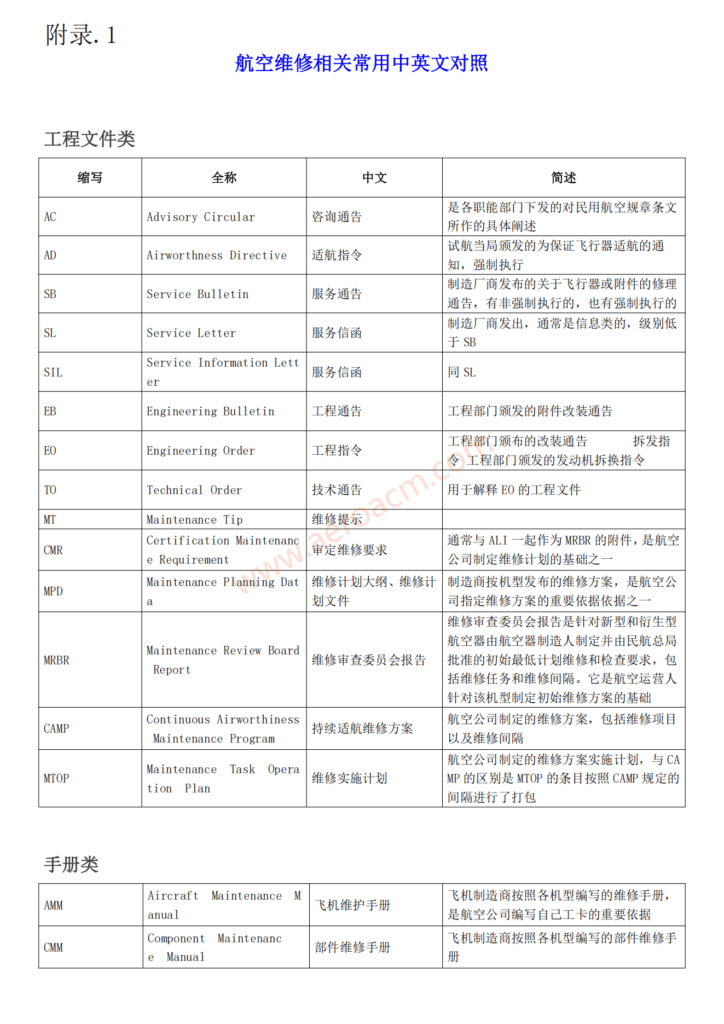
(1)涡喷发动机
Turbojet engine
单转子涡轮喷气发动机由进气道、压气机、燃烧室、涡轮、喷管组成,双转子涡轮喷气发动机有低压和高压两个转子。低压压气机和低压涡轮构成低压转子 N1;高压压机和高压涡轮构成高压转子 N2。双转子涡轮喷气发动机由进气道、低压压气机、高压压气机、燃烧室、低压涡轮、高压涡轮、喷管组成。部分军用发动机的涡轮和尾喷管间还有加力燃烧室。进气道将所需的外界空气以最小的流动损失送到压气机;压气机通过高速旋转的叶片对空气压缩作功,提高空气的压力;空气在燃烧室内和燃油混合燃烧,将燃料化学能转变成热能,生成高温高压的燃气;燃气在涡轮内膨胀,将燃气热能转变为机械能,驱动涡轮旋转,带动压气机;燃气在喷管内继续膨胀,加速燃气,燃气以较高速度排出,产生推力。
Single-rotor turbojet engine is composed of inlet, compressor, combustion chamber, turbine and nozzle. Double-rotor turbojet engine has low pressure and high pressure rotors. LP compressor and LP turbine form LP rotor N1; High pressure compressor and high pressure turbine form high pressure rotor N2. The twin-rotor turbojet engine is composed of inlet, low-pressure compressor, high-pressure compressor, combustion chamber, low-pressure turbine, high-pressure turbine and nozzle. Some military engines also have afterburner between turbine and tail nozzle. The inlet delivers the required outside air to the compressor with minimum flow loss; The compressor compresses the air through the high-speed rotating blades to improve the air pressure; Air is mixed with fuel in the combustion chamber to convert the chemical energy of fuel into heat energy and generate high temperature and high pressure gas; The gas expands in the turbine, converts the heat energy of the gas into mechanical energy, drives the turbine to rotate, and drives the compressor; The gas continues to expand in the nozzle, accelerates the gas, and the gas is discharged at a higher speed to generate thrust.
![图片[1]-燃气涡轮发动机的结构与原理Structure and Principle of Gas Turbine Engine【转】-航修札记](https://www.aeroacm.cn/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/image-12.png)
2)涡轮螺旋桨发动机
Turboprop engine
涡轮螺桨发动机由燃气涡轮发动机和螺旋桨组成。螺旋桨可由压气机轴直接驱动或由自由涡轮轴驱动。涡轮螺桨发动机的涡轮既带动压气机也带动螺旋桨,约 2/3 的涡轮功率用来转动压气机,其余的 1/3 用来转动螺旋桨和传动附件。
Turboprop engine consists of gas turbine engine and propeller. The propeller can be driven directly by the compressor shaft or by the free turbine shaft. The turbine of the turboprop engine drives both the compressor and the propeller. About 2/3 of the turbine power is used to rotate the compressor, and the remaining 1/3 is used to rotate the propeller and transmission accessories.
![图片[2]-燃气涡轮发动机的结构与原理Structure and Principle of Gas Turbine Engine【转】-航修札记](https://www.aeroacm.cn/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/image-13.png)
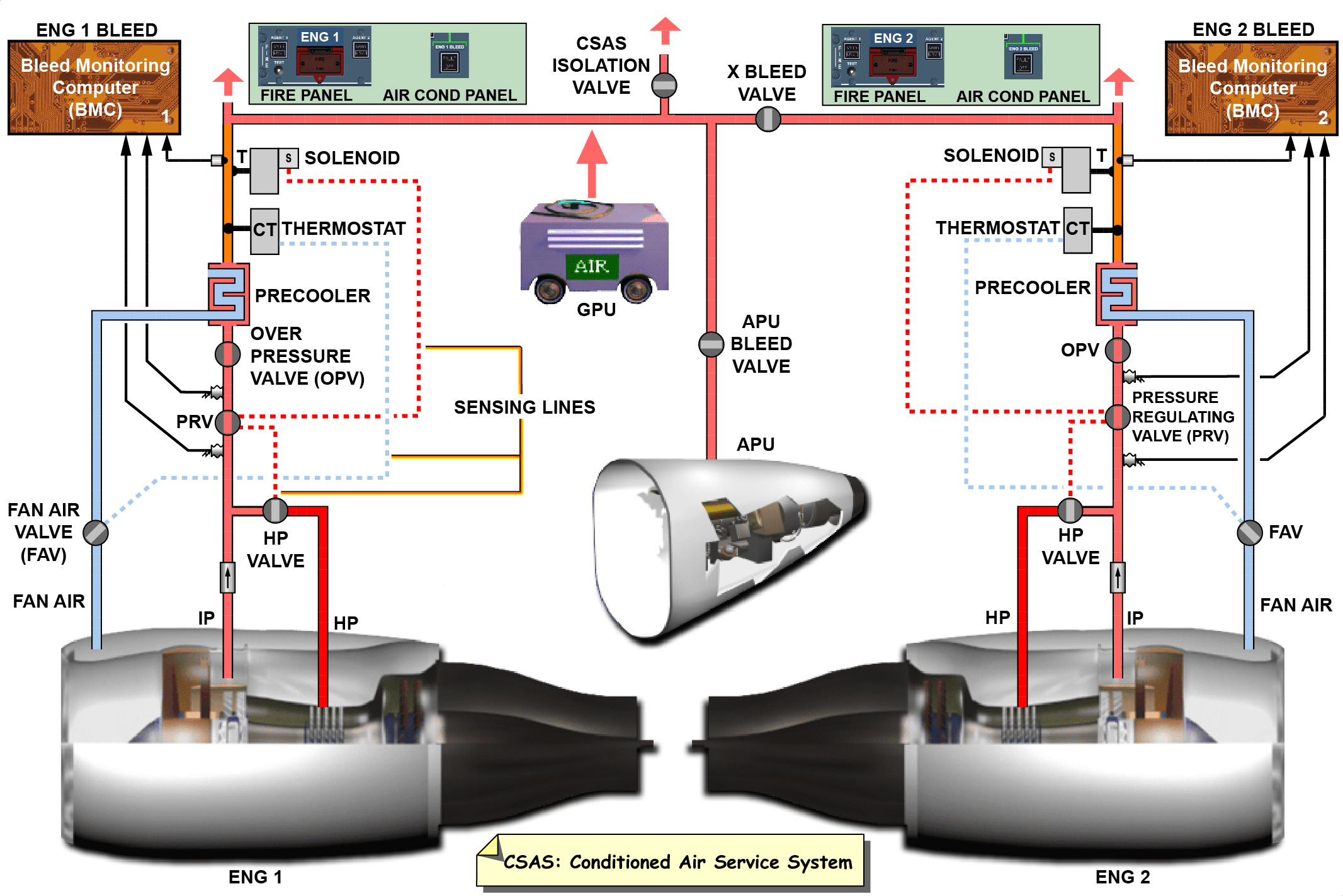
(3)涡轮风扇发动机
Turbofan engine
涡桨和涡扇的一个主要工作差别是通过涡扇发动机风扇的气流由扩张型进气道设计所控制,相对于风扇叶片的空气速度不被飞机的空速影响,这就消除了高空速下工作效率的损失,而高空速能力正是涡桨发动机的使用限制。另外,通过风扇的总空气流量比通过涡桨发动机的螺旋桨的要少,随着涡扇发动机涵道比增加,差别将减少。在高亚音速范围内,涡扇发动机具有推力大、推进效率高、噪音低、燃油消耗率低等优点。缺点是风扇直径大,迎风面积大,因而阻力大,发动机结构复杂,其速度特性不如涡喷发动机。它广泛应用于民航干线飞机。
One of the main working differences between turboprop and turbofan is that the air flow of the fan of the turbofan engine is controlled by the design of the expansion inlet, and the air speed relative to the fan blade is not affected by the airspeed of the aircraft, which eliminates the loss of working efficiency at high airspeed, and the high airspeed capability is the use limit of the turboprop engine. In addition, the total air flow through the fan is less than that of the propeller through the turbofan engine. With the increase of the bypass ratio of the turbofan engine, the difference will decrease. In the high subsonic range, the turbofan engine has the advantages of large thrust, high propulsion efficiency, low noise and low fuel consumption. The disadvantages are that the fan diameter is large, the windward area is large, so the resistance is large, the engine structure is complex, and its speed characteristics are not as good as the turbojet engine. It is widely used in civil aviation trunk aircraft.
![图片[3]-燃气涡轮发动机的结构与原理Structure and Principle of Gas Turbine Engine【转】-航修札记](https://www.aeroacm.cn/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/image-14.png)
涡扇发动机的风扇吸入的气流一部分如普通喷气发动机一样,送进压气机(称“内涵道”),另一部分则直接从涡喷发动机壳外围向外排出(称“外涵道”)。因此,涡扇发动机的燃气能量被分派到了风扇和燃烧室分别产生的两种排气气流上。这时,为提高热效率而提高涡轮前温度,可以通过适当的涡轮结构和增大风扇直径,使更多的燃气能量经风扇传递到外涵道,从而避免大幅增加排气速度。这样,热效率和推进效率取得了平衡,发动机的效率得到极大提高。发动机的效率高就意味着油耗低,飞机航程变得更远。
A part of the air flow sucked in by the fan of the turbofan engine is sent to the compressor (called “internal channel”) like the ordinary jet engine, and the other part is directly discharged from the periphery of the turbojet engine shell (called “external channel”), as shown in Figure 4. Therefore, the gas energy of the turbofan engine is distributed to the two exhaust streams generated by the fan and combustion chamber respectively. At this time, in order to improve the thermal efficiency and increase the temperature in front of the turbine, more gas energy can be transferred to the outer culvert through the fan through proper turbine structure and increasing the fan diameter, thus avoiding a significant increase in exhaust speed. In this way, the thermal efficiency and propulsion efficiency are balanced, and the efficiency of the engine is greatly improved. High engine efficiency means low fuel consumption and longer flight range.
![图片[4]-燃气涡轮发动机的结构与原理Structure and Principle of Gas Turbine Engine【转】-航修札记](https://www.aeroacm.cn/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/image-15-1024x873.png)
通过外涵的空气质量流量和通过内涵的空气质量流量之比称为涵道比。涵道比为 1 左右是低涵道比;涵道比为 2~3 左右是中涵道比;涵道比为 4 以上是高涵道比,目前民航上使用的大多是 5 以上的高涵道比涡扇发动机。涡扇发动机的推力由两部分组成,内涵产生的推力和外涵产生的推力。对于高涵道比涡扇发动机,风扇产生主要推力,占到 78%以上。
The ratio of the air mass flow through the outer culvert to the air mass flow through the connotation is called the culvert ratio. A culvert ratio of about 1 is a low culvert ratio; The culvert ratio is about 2~3, which is the medium culvert ratio; A bypass ratio of more than 4 is a high bypass ratio. At present, most turbofan engines with a bypass ratio of more than 5 are used in civil aviation. The thrust of a turbofan engine consists of two parts, the thrust generated by the connotation and the thrust generated by the connotation. For turbofan engines with high bypass ratio, fans generate the main thrust, accounting for more than 78%.
(4)涡轮轴发动机
Turboshaft engine
涡轮轴发动机作为直升机的动力,工作和构造上区别于涡喷和涡扇发动机,与涡桨发动机很相近。涡轮轴发动机同减速器系统一起能够驱动直升机的旋翼,以获得升力和气动控制力。当然涡轮轴发动机也有自己的特色——通常带有自由涡轮,而其他形式的涡轮喷气发动机一般没有自由涡轮。
As the power of helicopter, turboshaft engine is different from turbojet and turbofan engine in work and structure, and is very similar to turboprop engine. The turboshaft engine, together with the reducer system, can drive the rotor of the helicopter to obtain lift and aerodynamic control force. Of course, turboshaft engines also have their own characteristics – usually with free turbines, while other forms of turbojet engines generally do not have free turbines.
![图片[5]-燃气涡轮发动机的结构与原理Structure and Principle of Gas Turbine Engine【转】-航修札记](https://www.aeroacm.cn/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/image-16.png)


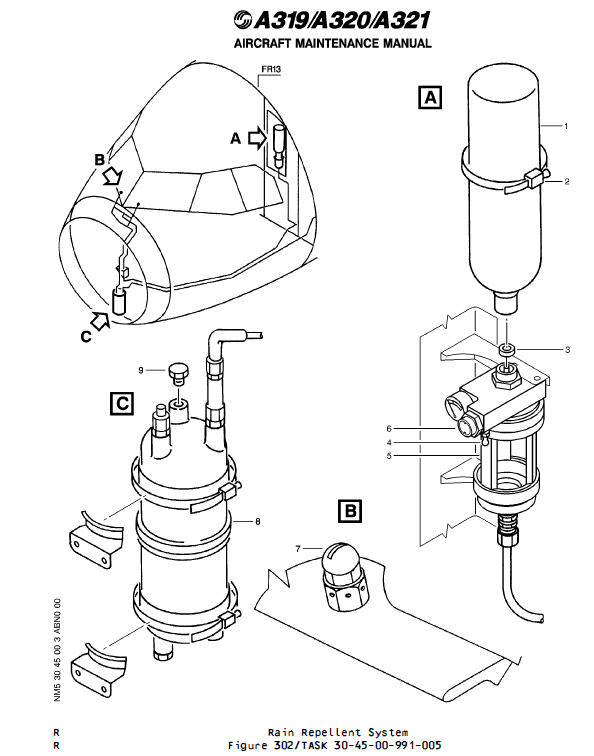
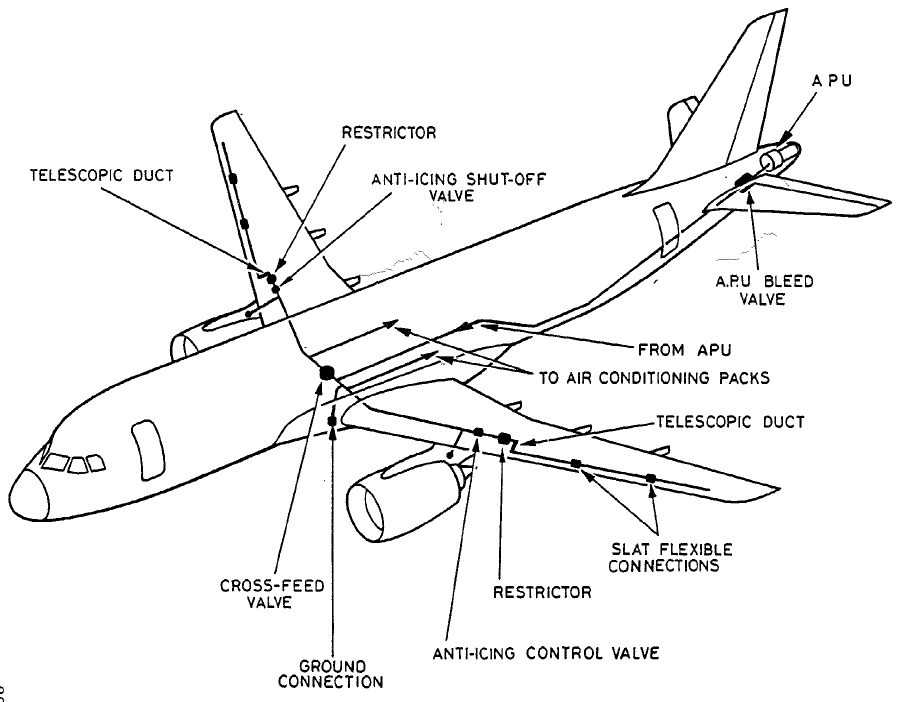
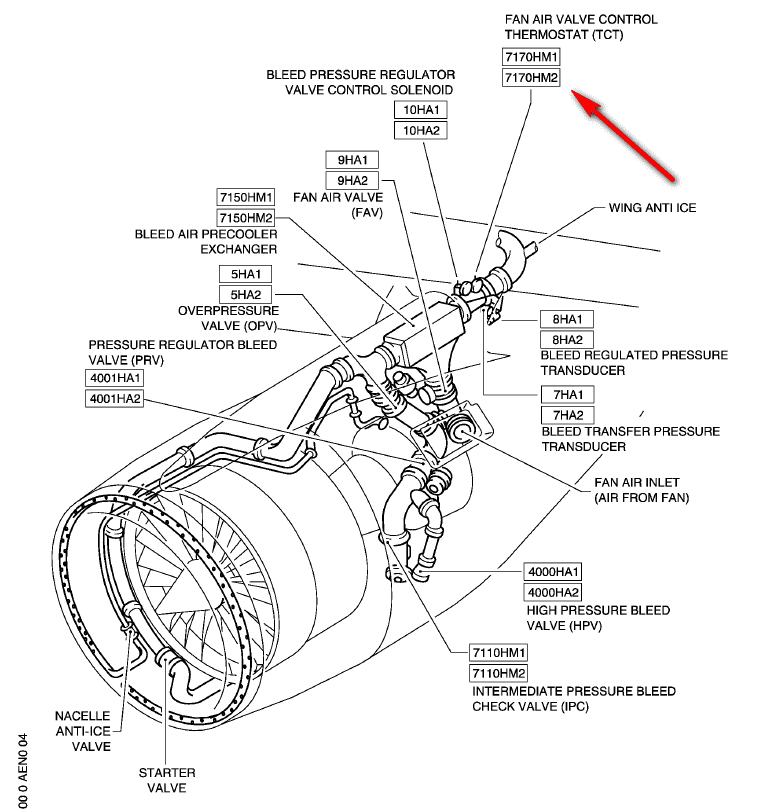
暂无评论内容